Wideband Delphi Estimation Technique Vs Planning Poker
Planning Poker is consensus based technique for estimating Product Backlog items or other things in Scrum. Usually teams estimate the relative size of items. Planning Poker results in reliable and efficient estimations because the team gains a common understanding about the items. Planning Poker is a variation of the Wideband Delphi method. The team then discusses the factors that influenced their estimates and proceed to a second round of estimation. This process is repeated until the estimates of individuals are close to each other and a consensus for the final estimate can be reached. Planning poker is one example of a Wideband Delphi technique. Wideband Delphi Technique. Wideband Variant of the Delphi Method was originated in the 1970s, by Barry Boehm and John A. The term 'wideband' is used because, compared to the Delphi Method, the Wideband Delphi Technique involved greater interaction and more communication between the participants.
Few teams actually use Wideband Delphi for their estimates. Most teams use one of its related techniques. That technique is planning poker. It's the most commonly used Agile estimation technique. Check out this course for an in-depth explanation of planning poker. One important detail is that the method requires that a group doing estimation come to a consensus agreement just like Wideband Delphi. Some people who describe Planning Poker allow for non-consensus estimates to be recorded.
- Estimation Techniques Tutorial
- Estimation Techniques Resources
- Selected Reading
Delphi Method is a structured communication technique, originally developed as a systematic, interactive forecasting method which relies on a panel of experts. The experts answer questionnaires in two or more rounds. After each round, a facilitator provides an anonymous summary of the experts’ forecasts from the previous round with the reasons for their judgments. Experts are then encouraged to revise their earlier answers in light of the replies of other members of the panel.
It is believed that during this process the range of answers will decrease and the group will converge towards the 'correct' answer. Finally, the process is stopped after a predefined stop criterion (e.g. number of rounds, achievement of consensus, and stability of results) and the mean or median scores of the final rounds determine the results.
Delphi Method was developed in the 1950-1960s at the RAND Corporation.
Wideband Delphi Technique
In the 1970s, Barry Boehm and John A. Farquhar originated the Wideband Variant of the Delphi Method. The term 'wideband' is used because, compared to the Delphi Method, the Wideband Delphi Technique involved greater interaction and more communication between the participants.
In Wideband Delphi Technique, the estimation team comprise the project manager, moderator, experts, and representatives from the development team, constituting a 3-7 member team. There are two meetings −

- Kickoff Meeting
- Estimation Meeting
Wideband Delphi Technique – Steps
Step 1 − Choose the Estimation team and a moderator.
Step 2 − The moderator conducts the kickoff meeting, in which the team is presented with the problem specification and a high level task list, any assumptions or project constraints. The team discusses on the problem and estimation issues, if any. They also decide on the units of estimation. The moderator guides the entire discussion, monitors time and after the kickoff meeting, prepares a structured document containing problem specification, high level task list, assumptions, and the units of estimation that are decided. He then forwards copies of this document for the next step.
Step 3 − Each Estimation team member then individually generates a detailed WBS, estimates each task in the WBS, and documents the assumptions made.
Wideband Delphi Estimation Technique Vs Planning Poker Strategy
Step 4 − The moderator calls the Estimation team for the Estimation meeting. If any of the Estimation team members respond saying that the estimates are not ready, the moderator gives more time and resends the Meeting Invite.
Step 5 − The entire Estimation team assembles for the estimation meeting.
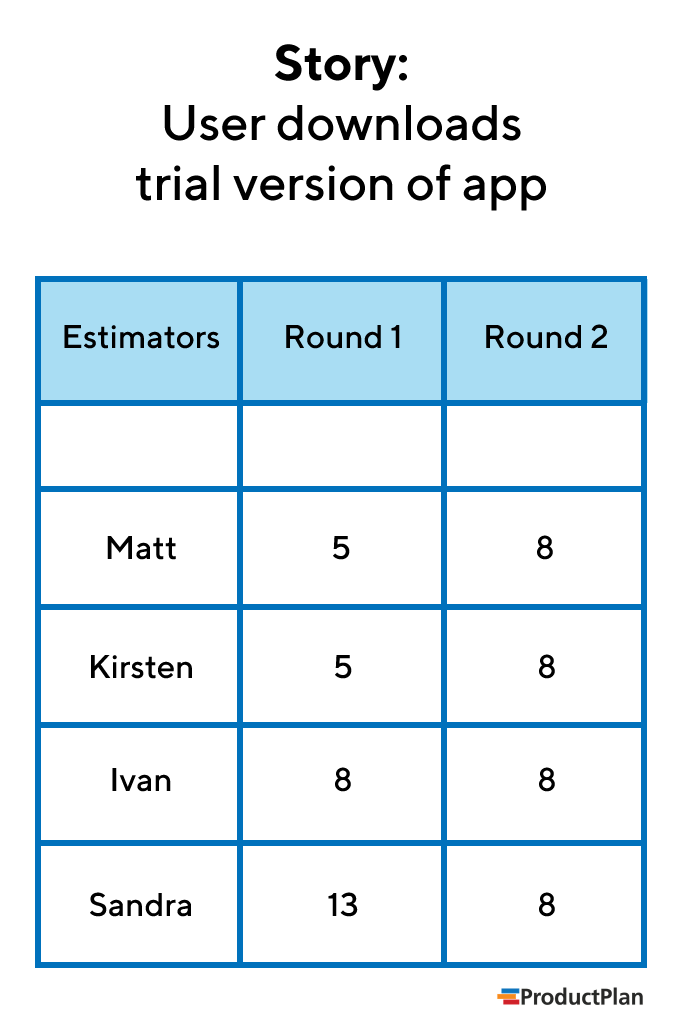
Step 5.1 − At the beginning of the Estimation meeting, the moderator collects the initial estimates from each of the team members.
Step 5.2 − He then plots a chart on the whiteboard. He plots each member’s total project estimate as an X on the Round 1 line, without disclosing the corresponding names. The Estimation team gets an idea of the range of estimates, which initially may be large.
Step 5.3 − Each team member reads aloud the detailed task list that he/she made, identifying any assumptions made and raising any questions or issues. The task estimates are not disclosed.
Wideband Delphi Estimation Technique Vs Planning Poker Software
The individual detailed task lists contribute to a more complete task list when combined.
Step 5.4 − The team then discusses any doubt/problem they have about the tasks they have arrived at, assumptions made, and estimation issues.
Step 5.5 − Each team member then revisits his/her task list and assumptions, and makes changes if necessary. The task estimates also may require adjustments based on the discussion, which are noted as +N Hrs. for more effort and –N Hrs. for less effort.
The team members then combine the changes in the task estimates to arrive at the total project estimate.
Step 5.6 − The moderator collects the changed estimates from all the team members and plots them on the Round 2 line.
In this round, the range will be narrower compared to the earlier one, as it is more consensus based.
Step 5.7 − The team then discusses the task modifications they have made and the assumptions.
Step 5.8 − Each team member then revisits his/her task list and assumptions, and makes changes if necessary. The task estimates may also require adjustments based on the discussion.
The team members then once again combine the changes in the task estimate to arrive at the total project estimate.
Step 5.9 − The moderator collects the changed estimates from all the members again and plots them on the Round 3 line.
Again, in this round, the range will be narrower compared to the earlier one.
Step 5.10 − Steps 5.7, 5.8, 5.9 are repeated till one of the following criteria is met −
- Results are converged to an acceptably narrow range.
- All team members are unwilling to change their latest estimates.
- The allotted Estimation meeting time is over.
Step 6 − The Project Manager then assembles the results from the Estimation meeting.
Step 6.1 − He compiles the individual task lists and the corresponding estimates into a single master task list.
Step 6.2 − He also combines the individual lists of assumptions.
Step 6.3 − He then reviews the final task list with the Estimation team.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Wideband Delphi Technique
Advantages
- Wideband Delphi Technique is a consensus-based estimation technique for estimating effort.
- Useful when estimating time to do a task.
- Participation of experienced people and they individually estimating would lead to reliable results.
- People who would do the work are making estimates thus making valid estimates.
- Anonymity maintained throughout makes it possible for everyone to express their results confidently.
- A very simple technique.
- Assumptions are documented, discussed and agreed.
Disadvantages
Wideband Delphi Estimation Technique Vs Planning Poker Rules
- Management support is required.
- The estimation results may not be what the management wants to hear.
Wideband Delphi Estimation Technique Vs Planning Poker For Dummies
The Wideband Delphi estimation method is a consensus-based technique for estimating effort. It derives from the Delphi method which was developed in the 1950-1960s at the RAND Corporation as a forecasting tool. It has since been adapted across many industries to estimate many kinds of tasks, ranging from statistical data collection results to sales and marketing forecasts.
Wideband Delphi Process[edit]
Barry Boehm and John A. Farquhar originated the Wideband variant of the Delphi method in the 1970s. They called it 'wideband' because, compared to the existing delphi method, the new method involved greater interaction and more communication among those participating. The method was popularized by Boehm's book Software Engineering Economics (1981). Boehm's original steps from this book were:
- Coordinator presents each expert with a specification and an estimation form.
- Coordinator calls a group meeting in which the experts discuss estimation issues with the coordinator and each other.
- Experts fill out forms anonymously.
- Coordinator prepares and distributes a summary of the estimates
- Coordinator calls a group meeting, specifically focusing on having the experts discuss points where their estimates vary widely
- Experts fill out forms, again anonymously, and steps 4 to 6 are iterated for as many rounds as appropriate.
A variant of Wideband Delphi was developed by Neil Potter and Mary Sakry of The Process Group. In this process, a project manager selects a moderator and an estimation team with three to seven members. The Delphi process consists of two meetings run by the moderator. The first meeting is the kickoff meeting, during which the estimation team creates a work breakdown structure (WBS) and discusses assumptions. After the meeting, each team member creates an effort estimate for each task. The second meeting is the estimation session, in which the team revises the estimates as a group and achieves consensus. After the estimation session, the project manager summarizes the results and reviews them with the team, at which point they are ready to be used as the basis for planning the project.
- Choose the team. The project manager selects the estimation team and a moderator. The team should consist of 3 to 7 project team members. The team should include representatives from every engineering group that will be involved in the development of the work product being estimated.
- Kickoff meeting. The moderator prepares the team and leads a discussion to brainstorm assumptions, generate a WBS and decide on the units of estimation.
- Individual preparation. After the kickoff meeting, each team member individually generates the initial estimates for each task in the WBS, documenting any changes to the WBS and missing assumptions.
- Estimation session. The moderator leads the team through a series of iterative steps to gain consensus on the estimates. At the start of the iteration, the moderator charts the estimates on the whiteboard so the estimators can see the range of estimates. The team resolves issues and revises estimates without revealing specific numbers. The cycle repeats until either no estimator wants to change his or her estimate or the estimators agree that the range is acceptable.
- Assemble tasks. The project manager works with the team to collect the estimates from the team members at the end of the meeting and compiles the final task list, estimates and assumptions.
- Review results. The project manager reviews the final task list with the estimation team.
See also[edit]
Further reading[edit]
- Andrew Stellman and Jennifer Greene (2005). Applied Software Project Management. Sebastopol, CA: O'Reilly Media. ISBN0-596-00948-8.